"Gravity storage" is now attracting attention as an adjustment force that is needed at the same time as the expansion of renewable energy. What is this old and new battery that uses potential energy?
Coordinating power essential for expanding renewable energy
In order for renewable energy and renewable energy to expand, their coordinating power is required. The more renewable energy there is, the more flexible adjustment power is needed when power cannot be generated (no sun, no wind, etc.). There are many possible types of flexibility. For example, wide-area operation of electricity, VPP, and, of course, electricity storage technology.
There are also some energy storage technologies (electric power storage technology / Energy Storage System). Pumped-storage hydropower is widely used on a large scale. In recent years, lithium-ion batteries, which are also used in EVs, are becoming more widespread. In terms of batteries, all-solid-state batteries are also under development.
Old and new technologies are attracting attention as the electricity storage technology. It is electricity storage by gravity. It uses the potential energy of gravity discovered by Newton. If a heavy object is in a high position, the potential energy will be high.
You don't have to think hard. The point is to use some energy to lift a heavy object from a low position to a high position. It is the storage of electricity by gravity that uses the energy generated when it falls from a high position to a low position. It is called Gravity Storage.
In fact, pumped-storage hydropower is the same. It uses electricity to lift water from the lower pond to the upper pond. This is electricity storage. To generate electricity, the turbine should be turned when water is dropped from the upper pond to the lower pond.
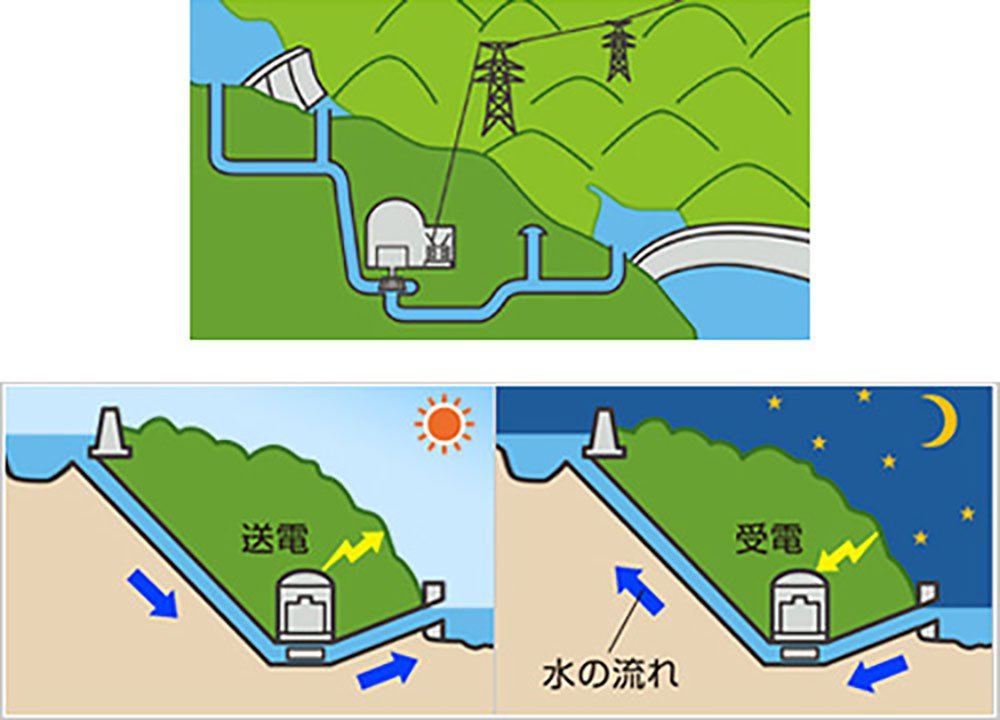
Energy storage technology that raises and lowers concrete blocks
Knowing this pumped-storage hydroelectric power generation, I came up with the idea that "this does not have to be water", started a gravity storage company as a venture, actually raised funds and made it a business, attracting worldwide attention. There is a company that is. An Energy Vault based in Switzerland and the United States.
Energy Vault uses a 35 ton concrete block instead of water. There are two methods of pulling up, one is a tower type. The other is a building type.
In the tower type, a crane is placed on the roof. Stack blocks with a crane (charging) and leave them in a high position until they are used (storage). When it is dropped down, the mechanical motor of the crane turns to generate electricity.
In the case of 35MWh, the height of the crane is 165m, and the blocks are stacked in a cylindrical shape like a ridge, so the diameter is 60m. It will be about a 30-story building. There are 6,000 to 7,000 blocks.
Concrete blocks are also used in the other building type. This is just like a multi-storey car park, with blocks lined up on the upper floors when charging. If you keep it, it will store electricity. When using it, drop it down. This system can be built in units of 10MWh and can be expanded to several GWh. This building type is 40% lower than the tower type.
Gravity storage that is environmentally friendly and can reduce costs ... Next page
Why environmental and supply chain risks are minimal
So far, Energy Vault has succeeded in raising funds from Softbank and others many times, and has been connected to the Swiss power grid as a demonstration experiment.
And in October of this year, Energy Vault announced that it had signed a contract with DG Fuels, a venture company for sustainable aviation fuel (SAF), green hydrogen production and diesel fuel production. It was decided to provide DG Fuels with 1.6 GWh of electricity storage equipment. Used in the green hydrogen production process of DG Fuels.
The deal expects Energy Vault to generate up to $ 520 million in revenue from the three projects. The first project is scheduled to begin in mid-2022.
The reason why DG Fuels finally chose Energy Vault is that it has the least environmental and supply chain risks. What this means is that this concrete block will be reused from excavated soil from construction sites, mine residue, coal fuel residues, and discarded wind turbine blades. It is made with the environment and footprint in mind from the construction materials. Moreover, the cost is low.
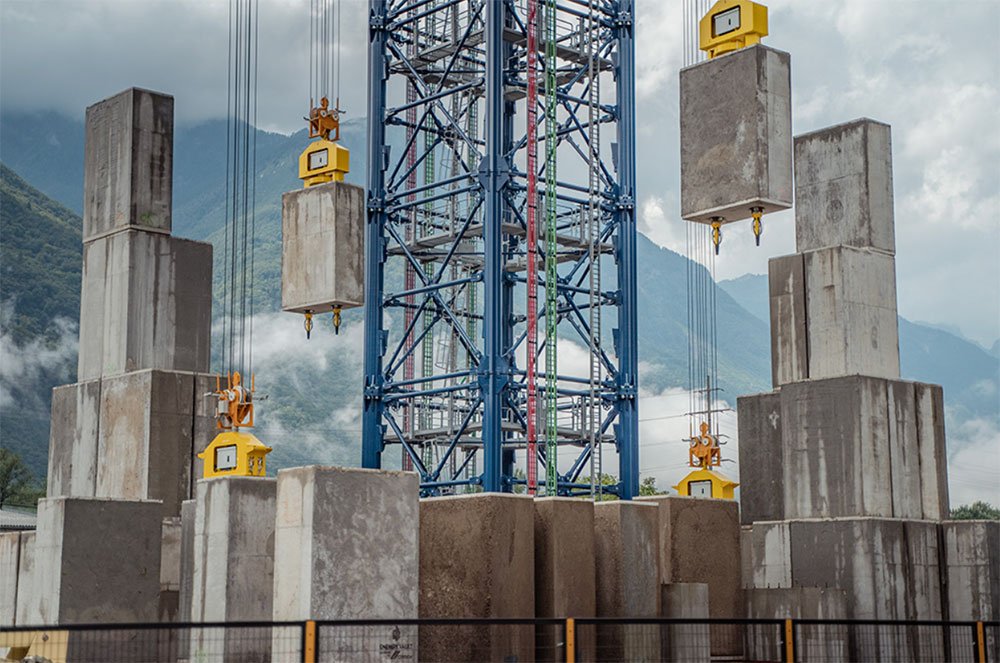

Concrete blocks are recycled materials
There is no need for mineral resources such as lithium-ion batteries, which also helps reduce costs. Moreover, this potential energy basically does not deteriorate with the passage of time. Power efficiency is more than 80%, which is more efficient than around 70% of pumped storage power generation.
Furthermore, the start-up time during power generation is several tens of seconds, which is shorter than that of pumped storage power generation. This short start-up time is also important for the ability to adjust renewable energy.
Above all, this technology consists of very "dead" technology. Block management is digital, but the basic technology of raising and lowering is a discovery of the 17th century. The robustness of this technology is also appreciated.
Energy Vault went public in September and launched a new technology division called Energy Vault Solution in November. We aim to improve efficiency by making full use of AI etc. with the optimum algorithm.
Pumped-storage hydropower is also a construction rush, and the introduction of electricity storage technology in Japan
Such energy storage technology is expanding with the expansion of renewable energy. Overseas, the construction rush has occurred since 2019, and the number of power generation facilities has increased 2.5 times. According to the US Department of Energy, 100 GW in China and 52.5 GW in the US will be installed in the next few years.
Of course, these energy storage technologies (like hydrogen) have "overflowing" renewable energy and show their value. However, even in Japan, it may be sufficiently useful in Kyushu and Hokkaido, where output restrictions are repeated. It is said that Kyushu Electric Power can use pumped-storage hydroelectric power generation for 2.3 GW, but it is not enough.
This gravity storage is cheaper to construct than pumped-storage hydropower, is more environmentally friendly and cheaper than lithium-ion batteries, is easy to construct, and is scalable. It may be in the limelight in Japan as well.








0 コメント:
コメントを投稿